Using peristaltic motion the carcinomatosis follows the peritoneal circulation and implants along the paracolic gutter passing back up into the undersurface of the diaphragm becoming implanted in morison s pouch the omental bursa and along the left paracolic gutter.
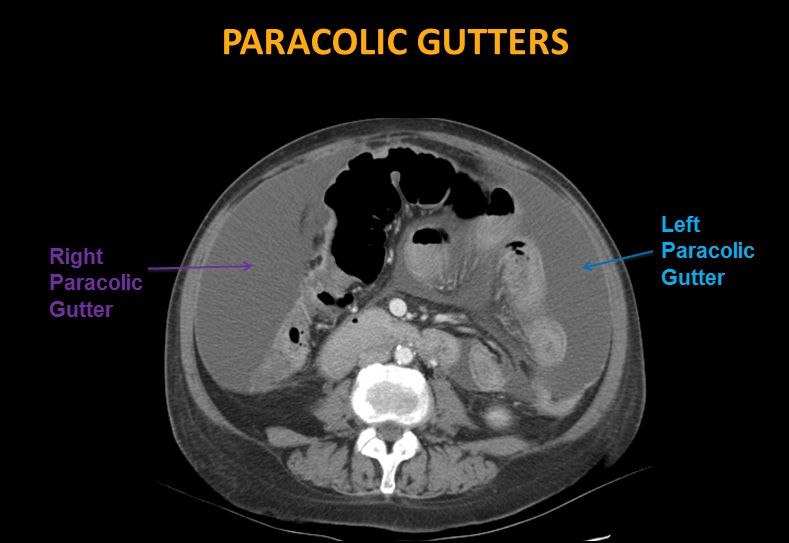
Paracolic gutters ct.
The right lateral gutter is much larger and allows for greater drainage than the left gutter.
The left lateral paracolic gutter.
This is why this patient also has a hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis ascites portal hypertension portacaval anastomosis and splenomegaly.
It can be compared to fluid in the gallbladder or stomach.
Fluid on ct is relatively hypodense dark on ct.
Download as powerpoint open in image viewer.
It is also known as sulci paracolic and paracolic recesses.
The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and communicates freely with the right subphrenic space.
Etiologically it means a channel adjacent to the abdominal wall.
It is the depression between the postero lateral wall of the abdomen and the lateral margins of the ascending and descending colon.
Paracolic gutters help keep infectious material away from the body s internal organs.
The paracolic spaces gutters are located lateral to the peritoneal reflections of the left and right sides of the colon fig 8a.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
The right lateral paracolic gutter.
Key signs of peritoneal carcinomatosis.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.
This allows the user to perfectly see the different parts of the peritoneal cavity omental bursa paracolic gutters mesentery mesocolon.
The paracolic gutters paracolic sulci paracolic recesses are spaces between the colon and the abdominal wall.
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
The inframesocolic space also contains paracolic gutters which are peritoneal recesses that are inferolateral extensions of their corresponding inframesocolic spaces on the posterior abdominal wall lateral to the ascending and descending colon respectively.
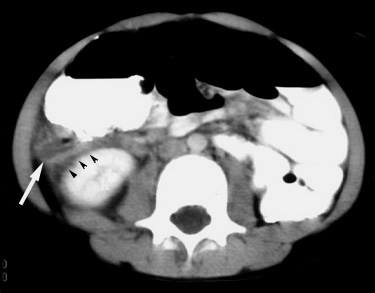
B contrast enhanced ct image at a lower level than a shows blood tracking laterally along the paracolic gutters arrows.
Both paracolic gutters run laterally along the back side of the abdominal wall and are situated between the abdominal wall and the outer margin of the colon.
Dense fluid may suggest hemoperitoneum especially in the context of trauma.